Heart: anatomy, structure and function
The function of the heart is to pump blood throughout the body. On its left side, the heart pumps oxygenated (arterial) blood to all organs and other parts of the body. The right side pumps venous blood to the lungs.
The human heart is located in the central part of the rib cage, slightly tilted to the left. It is located between the lungs and behind it are the esophagus and the aorta.
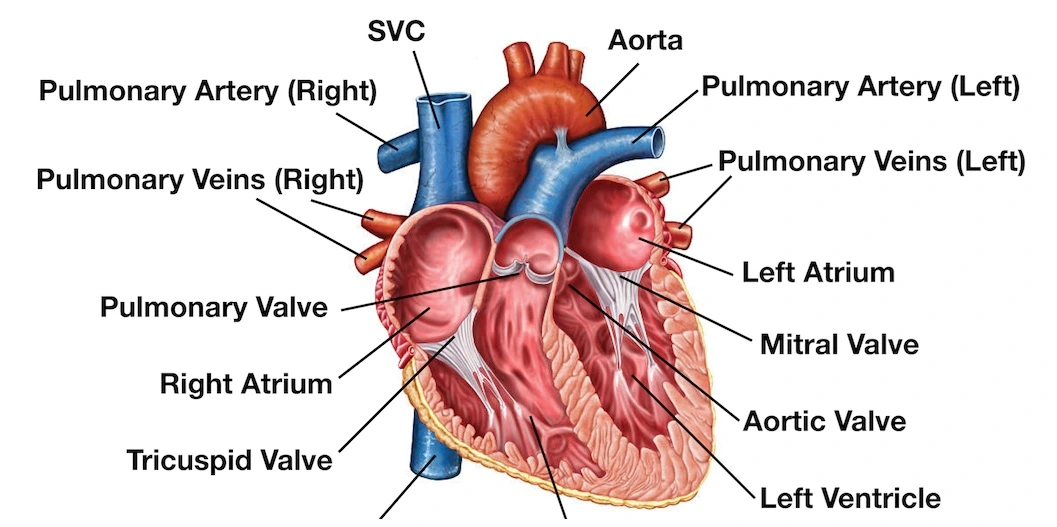
Anatomy and valves of the heart
The human heart is divided internally into four cavities:
- Two atria: Upper cavities through which blood reaches the heart;
- Two ventricles: Lower chambers through which blood leaves the heart.
The right atrium communicates with the right ventricle and the left atrium communicates with the left ventricle.
Between the atria and ventricles there are valves that regulate blood flow and prevent backflow, that is, the return of blood from the ventricles to the atria. These are called the right atrioventricular valve and the left atrioventricular valve.
For a long time, the atrioventricular valves were called tricuspid (right) and bicuspid or mitral (left).
Structure and layers of the heart
The heart wall is formed by three layers: pericardium, endocardium and myocardium.
Pericardium
The pericardium is the serous membrane that surrounds the heart. It is formed by two types of membranes with different compositions:
- Parietal or fibrous pericardium : Outer layer formed by a layer of collagen bundles.
- Visceral or serous pericardium : Inner layer formed by a serous membrane.
The pericardium has a protective function and helps the heart to remain in the correct position.
Endocardium
The endocardium is the thin, smooth membrane that lines the internal chambers of the heart. It is made up of flattened endothelial cells arranged in a single layer.
Myocardium
The myocardium is the middle and thickest layer of the heart. It is made up of striated muscle tissue and is responsible for the heart’s contractions. This condition allows the heart to perform its blood-pumping function.
Also learn about Muscle Tissue .
What is the function of the heart?
The heart’s primary function is to pump blood throughout the body .
To do this, it works like a double pump, its left side pumps oxygenated (arterial) blood to different parts of the body. Meanwhile, the right side pumps venous blood to the lungs.
Read also:
- Circulatory System
- Cardiovascular System
- Blood Vessels
- Veins
Heartbeat
The heart works by pushing blood through two movements:
- Systole: Contraction movement, in which blood is pumped to the body;
- Diastole: Relaxation movement, in which the heart fills with blood.
When the atria are filled with blood, they contract (systole), the valves open and blood is pumped into the relaxed ventricles (diastole).
The ventricles then contract (systole) and squeeze blood into the vessels. At this point, the atria in diastole fill with blood. This set of movements is called the cardiac cycle .
The sound we hear from the heartbeat corresponds to the movement of the valves, which occurs in a rhythmic manner.
- In an adult at rest, the heart beats about 70 times per minute ;
- In a child the heart normally beats about 120 times per minute ;
- In a baby the heart normally beats 130 times per minute.
Blood pressure
Each time the ventricles contract, they push blood into the arteries .
As the blood is pumped, it puts pressure on the walls of the blood vessels, which expand and contract.
This pulse is called arterial pressure or pulse , through which the frequency of the heartbeat can be verified.
Hypertension occurs when blood pressure reaches high levels and remains that way for a long period of time.
It generally does not cause symptoms, but it increases the risk of stroke, heart attack and other cardiovascular system problems.
Read also about:
- Blood pressure
- Hypertension
- Hypotension
Curiosities
- In the human body, only the corneas are not supplied with blood.
- The blue whale is the living being with the largest heart, weighing up to 680 kg.
- If the heart has a sufficient supply of oxygen, it can continue beating even outside the body. This condition allows transplants to be performed.